Authors: Jing Dong, Qiongxin Liang, Yun Niu, Shengjun Jiang, Li Zhou, Jinmei Wang, Changyang Ma, Wenyi Kang
Journal: International Journal of Biological Macromolecules
September 2020, Volume 159, Issue 15, 725-738
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.042
中文简介:http://syj.henu.edu.cn/info/1061/1087.htm
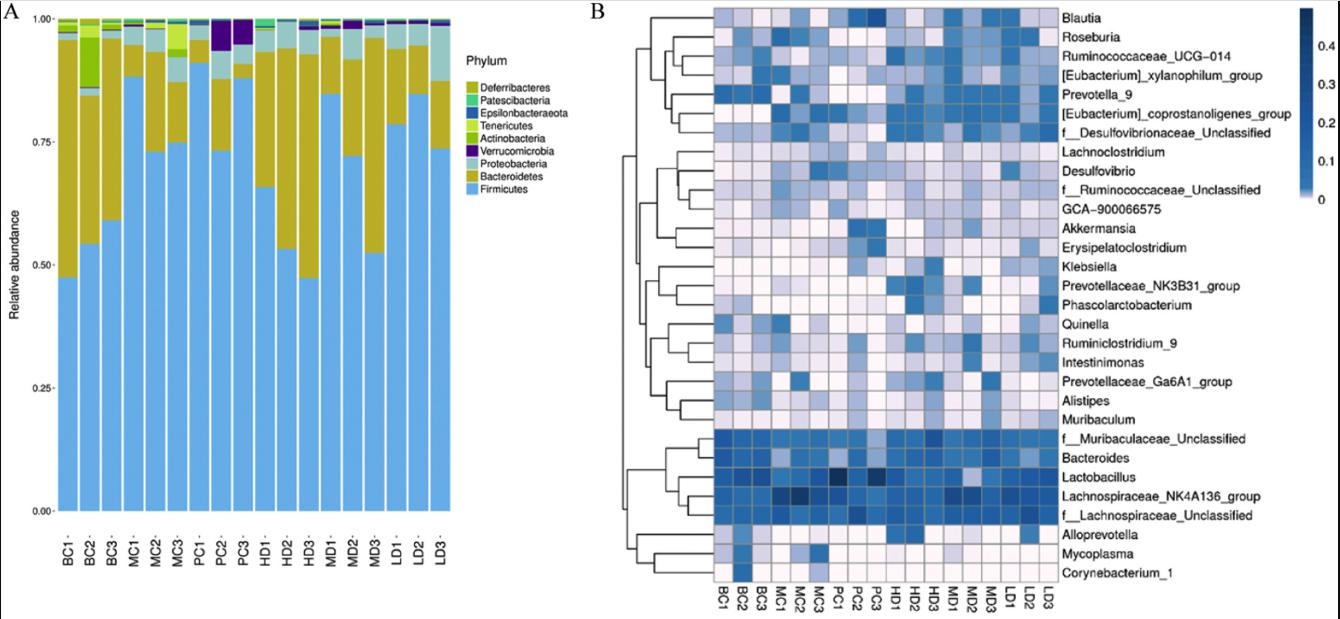
Effect of Nigella sativa seed polysaccharides (NSSP) on type 2 diabetic mice and its gut microbiota was investigated on the type 2 diabetic mice model feed by high-fat diet. Fasting blood glucose (FBG), biochemical parameters, expression levels of cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and phosphor-AKT (p-AKT) protein, membrane glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) in skeletal muscles, as well as the change of gut microbiota profile in mice model were measured. Results showed that the high-dose NSSP could significantly lower the levels of FBG, glycosylated serum protein (GSP), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), malondialdehyde (MDA), TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β, and significantly increased insulin (INS), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and the expression levels of p-AKT and GLUT4 in mice. Besides, the high-dose NSSP has significantly increased the abundance of f_Muribaculaceae_Unclassified and Bacteroides, which were significantly suppressed in the mice gut after the treatment of streptozotocin (STZ). These results indicated that NSSP could improve the abnormal state of diabetic mice by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway with simultaneous changes of the gut microbiota profile.